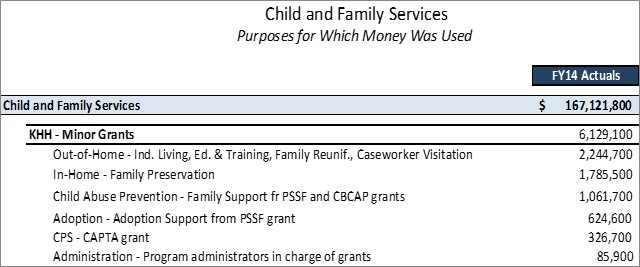
Minor Grants refers to the small grants awarded DCFS, as opposed to the major grants such as titles IV-B (child welfare), IV-E (foster care/adoption assistance), XIX (Medicaid), and XX (Social Services Block Grant) of the federal Social Security Act. These minor grants are usually administered by program managers at the state office rather than by the various regions.
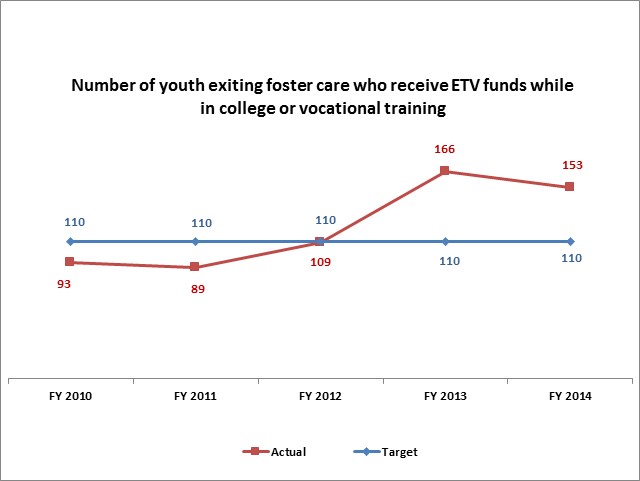
Regarding the positive trend greater than 5% in the Number of children and parents receiving crisis/respite services from the DCFS Facility Based Services program performance measures, the agency states, "There are efforts to maximize the number of youth who receive the educational training vouchers."
Currently, this program includes the following grants:
- Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act (CAPTA) Grant: The purpose of this grant is to reduce child abuse and neglect by providing leadership in statewide prevention efforts and supporting community-based child abuse prevention and family support programs. Current grant funding provides for child abuse prevention and family support programs through contract, including a child abuse prevention program manager, support of child abuse prevention network activities, evaluation of prevention program outcomes, and support for a statewide conference on child abuse and neglect.
- Promoting Safe and Stable Family Grants (authorized through Title IV-B, Part II, of the federal Social Security Act): These funds provide family preservation, family support, time-limited family reunification efforts, and adoption promotion and support services. Family support projects have been funded in communities throughout the state, one of which offers new evidence-based services to clients receiving in-home services statewide as part of the DCFS efforts to strengthen in-home services. DCFS regions also provide family preservation, reunification, and adoption support services.
- Transition to Adult Living: Two grants support the Transition to Adult Living Program (TAL), including the Chafee Foster Care Independent Program and the Education and Training Voucher Program (authorized by Section 477 of the federal Social Security Act). TAL assists youth 14 years and older to prepare to transition successfully from foster care to adult living. The program includes mentoring, skills development, educational support, employment preparation, and financial support for post-secondary education and training for older youth that have already aged out of foster care or who were adopted at the age of 16 or older from foster care. This program also provides support and resources for youth 18 to 21 that have exited from foster care.
- Community Based Child Abuse Prevention (CBCAP) Grant: - provides funding to reduce child abuse and neglect by providing leadership in statewide prevention efforts and supporting community-based child abuse prevention and family support programs.
- Education and Training Voucher (ETV) Grant: - provides financial support for post-secondary education and training for youth who have aged out of foster care at age 18 or older or who are adopted at age 16 or older.
- Promoting Safe and Stable Families (PSSF) Caseworker Visitation: - provides funding to support monthly caseworker visits to children in foster care, with an emphasis on improving caseworker decision-making on safety, permanency, and well-being of foster children and on activities designed to increase retention, recruitment, and training of caseworkers.
- Adoption Incentive Grant: - provides funding to qualified states that increased the number of foster child adoptions, special needs adoptions, and older child adoptions in a given year to support adoption of children who cannot safely return home from foster care and to strengthen state child welfare systems. Grant funds may be used for child welfare services that are allowable under Titles IV-E and IV-B of the Social Security Act. Adoption Incentive Grant Funds are provided to states that have qualified for funding due to an increase in the number of children from foster care, special needs adoptions, or adoptions of older children. These funds are provided to states that are performing well as a means to help strengthen their child welfare systems. Grant funds may be used for child welfare services and administrative functions that allowable under Titles IV-E and IV-B of the Social Security Act. Since the amount of funding is not predictable, the grant is generally not used to fund large, ongoing program activities. DCFS currently plans to use these funds to strengthen in-home programs and services, support efforts that will reduce the number of children in foster care, provide post-adoption support for children with extreme needs, provide training on child welfare topics, provide technology resources for staff as recommended by legislative auditors, and provide additional resources for modernization of SAFE (the DCFS child welfare information system).
- Family Violence Prevention Services Grant: - provides funding for shelter and supportive services for victims of domestic violence and their dependents and for public awareness about domestic violence, including funding a statewide domestic violence hotline.
COBI contains unaudited data as presented to the Legislature by state agencies at the time of publication. For audited financial data see the State of Utah's Comprehensive Annual Financial Reports.