The Bureau of Children with Special Health Care Needs encompasses eight programs serving special needs children: Fostering Healthy Children, Developmental Consultative Services, Utah Birth Defect Network, Newborn Screening Program, Specialty Services Program, Neonatal Follow-up Program, Child Health Advanced Records Management, and Technology Dependent Waiver/Family Involvement. Children with Special Health Care Needs programs work to reduce preventable death, disability, and illness due to chronic and disabling conditions by providing access to affordable high-quality health screening, specialty health care, and coordination of health services. Bureau programs try to improve the system of care for Utah children with special needs through direct or population-based services and the promotion of system infrastructure building.
During the 2015 General Session, the Legislature appropriated for Fiscal Year 2016, $10,377,300 from all sources for Children with Special Health Care Needs. This is a 13.4 percent reduction from Fiscal Year 2015 revised estimated amounts from all sources. The total includes $606,600 from the General/Education Funds, a reduction of 0.2 percent from revised Fiscal Year 2015 estimates.
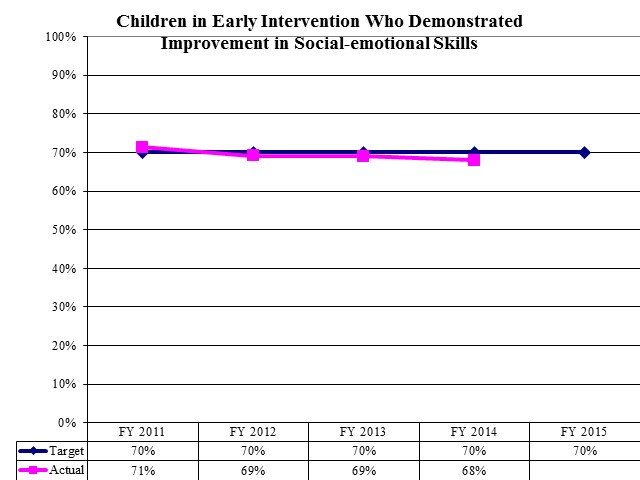
Children in Early Intervention Who Demonstrated Improvement in Social-emotional Skills
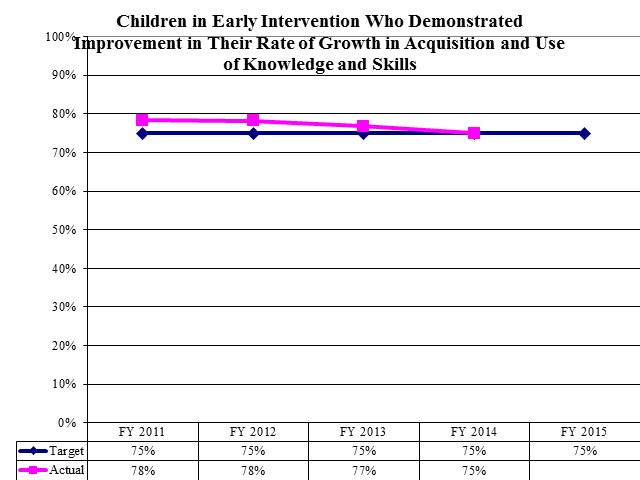
Children in Early Intervention Who Demonstrated Improvement in Their Rate of Growth in Acquisition and Use of Knowledge and Skills
Children in Early Intervention Who Demonstrated Improvement in Their Rate of Growth in the Use of Appropriate Behaviors to Meet Their Needs

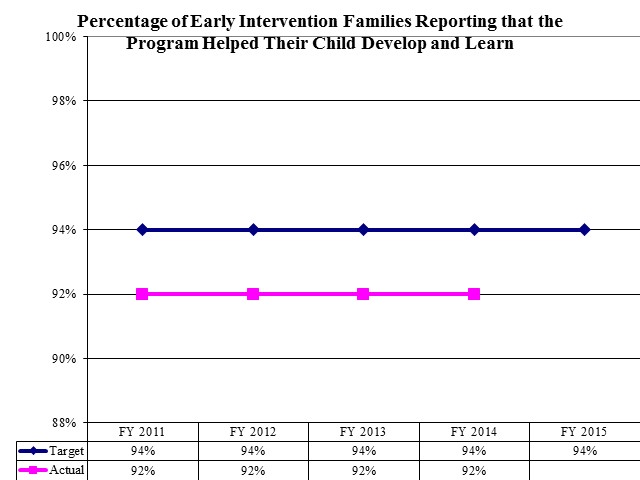
Percentage of Early Intervention Families Reporting that the Program Helped Their Child Develop and Learn
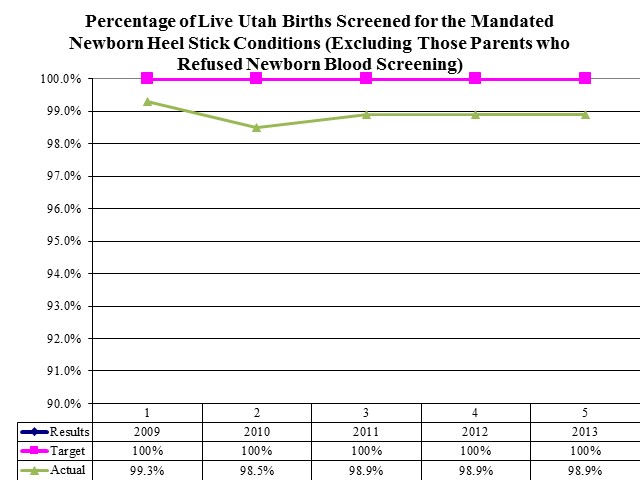
Percentage of Live Utah Births Screened for the Mandated Newborn Heel Stick Conditions (Excluding Those who Parents Refused Newborn Blood Screening)
- Goal: Meet the health care needs of children in the Utah Child Welfare System in a timely manner.
- Target Population: All children in the Utah Child Welfare System.
- Services Provided: Due to a 1994 court settlement agreement the State is required to provide medical, dental, and mental health care to all children in foster care custody on an ongoing basis. Additionally, the State must make sure they receive any follow up care deemed necessary by their medical providers and refer children with developmental delays noted on the Ages and Stages Questionnaire to Early Intervention.
- Delivery System: The Division of Child and Family Services in the Department of Human Services contracts this service with the Department of Health to provide coordination of Medicaid services for all children entering foster care across the State. The Department of Health uses registered nurses to coordinate the healthcare of youth in foster care.
Developmental Consultative Services
- Goals:
- Recognize the need for early diagnosis and treatment
- Provide timely detection of sensory, cognitive, and emotional disorders
- Assist the family in identifying their child's strengths and weaknesses
- Develop and monitor a written plan of service
- Provide parents with support and information
- Coordinate the delivery of services with local agencies
- Promote and develop appropriate community-wide services for the prevention of disabilities
- Target Population: children birth to 18 years of age who have developmental disabilities or chronic illness associated with developmental delay.
- Services Provided: developmental assessment services and access to multi-disciplinary medical services such as pediatric, genetic, neurological, psychological, speech, occupational/physical therapy, social work/case management evaluations, and support.
- Delivery System: services offered in the Salt Lake, Ogden, and Logan areas as well as itinerant clinics coordinated with the local health departments at the following sites: Blanding/Montezuma Creek, Moab, Price, Richfield, St. George, and Vernal.
The Utah Birth Defect Network is a statewide surveillance system monitoring the occurrence of major structural birth defects in Utah. The Utah Birth Defect Network uses this information to assess the prevalence of birth defects occurring in Utah; conduct epidemiological studies to determine risk factors; educate women and health care providers about these risk factors; evaluate whether education has decreased specific birth defects; and respond to reported clusters of birth defects. Birth defects are the leading cause of infant mortality, contribute to premature births, and are the major reason for hospitalizations during the first year of life. There are economic costs to families and society for children born with birth defects and the costs extend beyond medical and surgical care to behavioral and educational service issues. Because the cause of most birth defects is unknown, Utah Birth Defect Network participates in a national study of birth defects to increase understanding of modifiable risk factors.
The Utah Birth Defect Network's works toward primary prevention of birth defects by monitoring occurrence, conducting educational outreach, and participating in collaborative epidemiologic studies. Evaluation of the Utah Birth Defect Network epidemiologic data provides information in order to assess risk factors for birth defects and develop primary prevention activities directed at reducing these risk factors. Primary prevention activities target high-risk populations. The continuous tracking of all major birth defects statewide provides an evaluation of the effectiveness of the prevention programs. The Utah Birth Defect Network serves as a resource and referral system for families and physicians.
- Goal: Provide rapid identification of all newborn screening test results for 38 diseases within 24 to 72 hours. Utah does not process tests during weekends.
- Target Population: All newborns.
- Services Provided: Statewide system for early identification and referral of newborns with certain metabolic, endocrine, or hematologic disorders that can produce long-term mental or physical disabilities or death if not treated early. The disorders are: congenital hypothyroidism, galactosemia, cystic fibrosis, hemoglobinopathy, biotinidase, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, amino acid disorders, fatty acid disorders, and organic acid disorders. Services include education and counseling to families of an affected newborn.
- Delivery System: Developing and dispersing newborn screening kits. Training and educating institutions of birth (hospitals, birthing centers, midwives) on the importance of screening, screening practices, proper collection techniques and submission parameters. Reporting abnormal screening results to medical home (provider) and providing education/direction on follow-up needs for each specific disorder. Coordinating any necessary testing beyond the screening test to identify a possible disease.
- Goal: help assure optimal development in Utah's children with special needs, through a collaborative statewide system of education, prevention, early identification, early intervention, and care coordination.
- Target Population: children under age 8 with special health care needs.
- Services Provided: statewide screening, evaluation, and referral of infants and children with hearing, speech, vision, motor, movement, and transition problems. Once testing identifies a problem, children receive referrals to appropriate local resources for continued management. Public education, professional education, consultation, and technical assistance are also available. Specialty Services also oversees the legislatively mandated hearing screening of all Utah newborns. Hospital screening programs and audiologists receive help tracking and following up with infants that require additional testing.
- Delivery System: clinical facilities in Salt Lake City and Price as well as rural clinics held in cooperation with local health departments. Charges vary based on ability to pay, utilizing a sliding fee schedule. Clinics deny no services due to a family's inability to pay.
- Goals:
- Improve long-term outcome by identifying and treating significant findings in a timely fashion
- Coordinate services with existing resources and partner in long-term care
- Provide feedback to Utah newborn intensive care units and allow for reassessment of treatment practices
- Ultimately reduce cost of family stress, health care, and educational resources
- Target Population: Very low birth weight babies. Of the extremely low birth weight babies, 44% will need special education resources, 33% will test in the mentally retarded range, and 13% will have cerebral palsy.
- Services Provided: Two and one half years of follow-up for the very low birth weight babies. Four and one half years of follow-up for the extremely low birth weight babies. Follow up includes periodic screening by multiple providers (neurologist, ophthalmologist, pediatrician, audiologist, speech pathologist, dietitian, psychologist, occupational/physical therapist, social worker, and nurse).
- Delivery System: Clinics in Salt Lake City, Ogden, and Provo.
Child Health Advanced Records Management (CHARM)
Currently, data exists in an array of public and private health sectors and each database serves its own users, but with no capacity to share data across organizations or health programs. This lack of coordination typically does not provide a network of care for families and results in many children not receiving critical follow-up. The Child Health Advanced Records Management (CHARM) Project is a coordinated, Department-wide effort to create an electronic virtual health profile for every child in Utah that allows real-time digital access and data sharing among appropriate health care programs and partners. The CHARM vision is to create a shareable repository of child-specific public health information with secure role-based confidential access to a comprehensive set of integrated public health data accessible by people with a need to know, that promotes timely and efficient access to needed services, and supports program planning and evaluation. Integrating the State's health care databases provides for immediate access to information that is stored in specific databases to track and monitor health status for children and their families.
In the last few years, CHARM has linked the databases from Vital Records, (Birth and Death Certificates), Utah Statewide Immunization Information System, Early Hearing Detection and Intervention, Baby Watch Early Intervention Program, the Office of Recovery Services, Newborn Screening (heelstick) Program, the Utah Birth Defect Network, and clinical information from the Neonatal Follow-up Program. In the near future CHARM will link to the Master Person Index. Through data-sharing and tracking among integrated programs, CHARM's goal is to reduce the number of children lost to follow up statewide and provide more accurate and timely information to the child's medical home through web access. The Department is developing strategic and technical implementation plans to incorporate the CHARM data integration system into the Utah statewide Department's Clinical Health Information Exchange (cHIE) initiative.
Funding for this project has come from braiding multiple funding streams including Health Resources Services Administration grants, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention grants, and the Maternal and Child Health Block Grant. Management of the funds is performed by an oversight committee (CHARM Governing Board) to ensure accountability and coordinated use. The CHARM Project is managed by a "hands on" work group consisting of a program manager, an operations manager, and technical data services and support.
Technology Dependent Waiver/Family Involvement
The Division of Medicaid and Health Financing shares the responsibility for the day-to-day administrative activities for Utah's Waiver for Technology Dependent, Medically Fragile Individuals with the Technology Dependent Waiver Program. The waiver program tries to prevent institutionalization and to facilitate transition from an institutional setting to a home and community-based setting for technology dependent, medically-fragile children with complex medical conditions.
The Family Involvement Program/Family Voices provides information, training, and support regarding health care and community services to families of children and youth with special health care needs. Family Voices facilitates partnerships between families and professionals on behalf of children and youth with special health care needs.
The monthly caseload is the number of children served in the Baby Watch program.
COBI contains unaudited data as presented to the Legislature by state agencies at the time of publication. For audited financial data see the State of Utah's Comprehensive Annual Financial Reports.