The Bureau of Epidemiology is responsible for: (1) the detection, investigation, and control of communicable and infectious diseases, (2) surveillance and investigation of health effects associated with environmental hazards, (3) coordinating a statewide environmental sanitation program including 15 sanitation rules, (4) supporting treatment of HIV, AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome), sexually transmitted disease, and tuberculosis, and (5) managing a statewide immunization program and immunization information system.
During the 2015 General Session, the Legislature appropriated for Fiscal Year 2016, $22,596,300 from all sources for Epidemiology. This is a 10 percent reduction from Fiscal Year 2015 revised estimated amounts from all sources. The total includes $2,835,100 from the General/Education Funds, an increase of 1.5 percent from revised Fiscal Year 2015 estimates.
In addition to statewide compensation and internal service fund cost increases, the following appropriation adjustments were made during the 2015 General Session:
Here is the November 2013 press release from the Department of Health regarding the increase in gonorrhea cases - http://udohnews.blogspot.com/2013/11/gonorrhea-cases-up-94-percent-in-utah.html.
In FY 2015 the Department of Health is investigating a cluster of infant mortalities in the Tri-County Health Department counties of Daggett, Uintah, and Duchesne.
Accidental/Undetermined Overdose Deaths Due to Strictly Legal Drugs
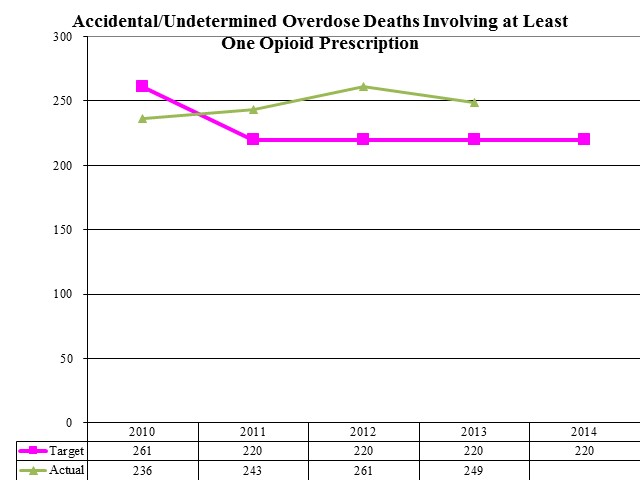
AIDS Cases Among Those Ages 13+ per 100,000 Population
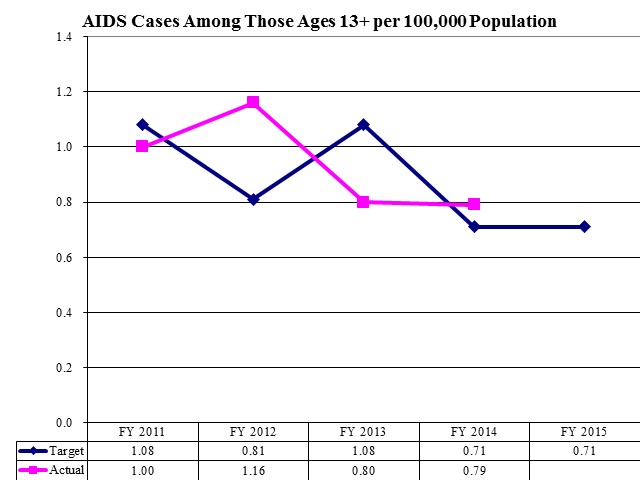
Gonorrhea Cases per 100,000 Population
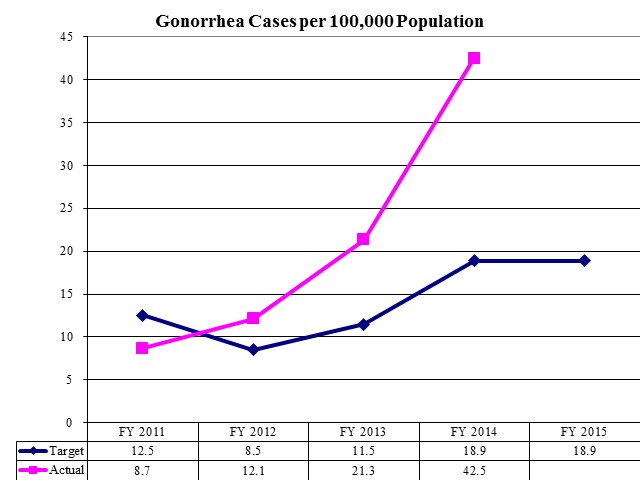
HIV-related Deaths per 100,000 Population
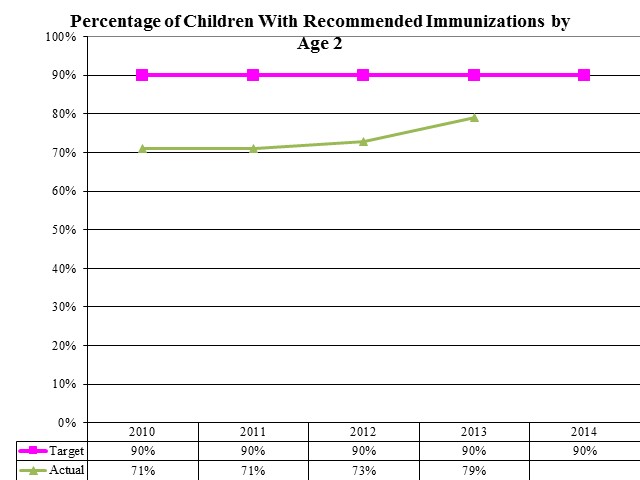
Percentage of Children With Recommended Immunizations by Age 2
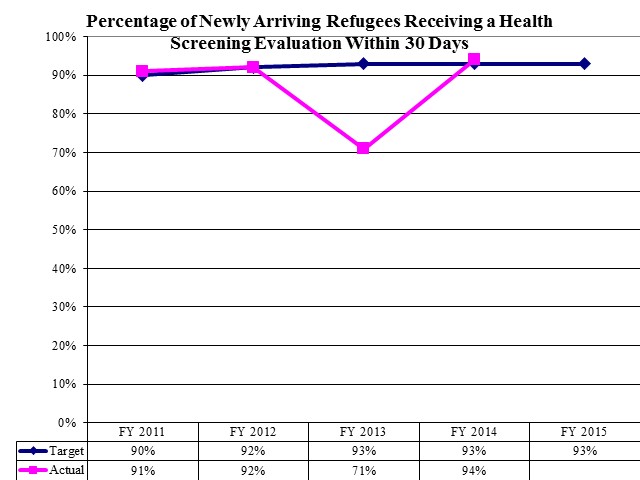
Percentage of Newly Arriving Refugees Receiving a Health Screening Evaluation Within 30 Days
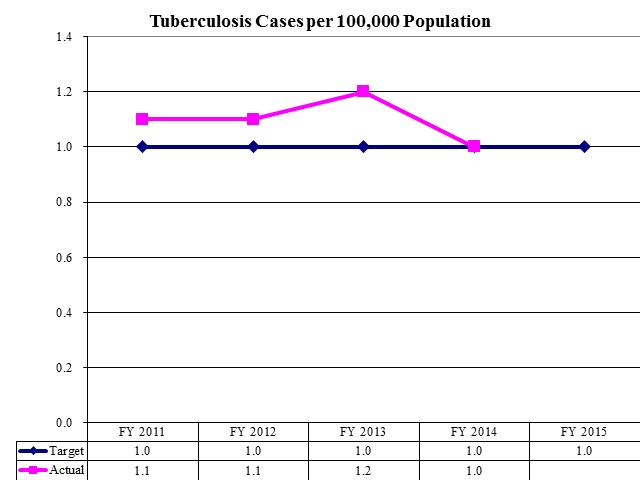
Tuberculosis Cases per 100,000 population
The Bureau operates nine programs: the Communicable Disease Prevention Program, the Treatment and Care Services Program, the Communicable Disease Investigation and Response Program, the Environmental Epidemiology Program, the Environmental Sanitation Program, the Immunization Program, the Communicable Disease Analysis and Reporting Program, the Utah Statewide Immunization Information System, and the Healthcare Associated Infections Prevention and Reporting Program. The programs have adopted the U.S. Healthy People 2020 Goals and Objectives, and activities are established to meet Health Department goals of protecting the public health, improving quality of life, preventing disease and premature death, and promoting healthy lifestyles for the residents of the State.
The Bureau also is responsible for developing and operating surveillance systems to detect bioterrorism and for assuring epidemiological preparedness to respond to an incident of bioterrorism or the similar threat of pandemic disease. Funding sources include the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Health Resources Services Administration, Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists, and the Utah Department of Workforce Services.
The Department of Health requires reporting by laboratories and medical providers 20 diseases within 24 hours and nearly 60 diseases within 72 hours in accordance with UCA 26-6-6. The Department also requires reporting of three multi-drug resistant organisms.
UCA 26-6-31 directs the Department of Health to annually prepare and publicly disclose a report on selected health care associated infection rates. The rates are for the following types of medical facilities: ambulatory surgical facility, general acute hospital, end stage renal disease facility, and specialty hospital. The National Healthcare Safety Network in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention requires the reporting of certain types of infections.
Communicable Disease Prevention Program
- Goals: Decrease the annual incidence rate and rate of transmission of HIV, sexually transmitted diseases, and hepatitis C. Decrease risky sexual and drug-using behaviors among persons at high-risk for acquiring sexually transmitted diseases. Increase the proportion of HIV-infected people aware of their infection. Increase the proportion of sexually transmitted diseases-infected persons who receive treatment for themselves and their sexual partners. Increase the proportion of HIV/ hepatitis C-infected persons linked to prevention and care services.
- Target Population: Individuals at high risk of contracting HIV (men who have sex with men, youth, women, injecting drug users, and ethnic populations), persons ages 15-24 (group most likely to have sexually transmitted diseases), youth detention centers, homeless youth, and youth in substance abuse treatment centers.
- Services Provided: Confidential or anonymous pre- and post-test HIV counseling, testing and referral services to targeted individuals at publicly-funded sites (local health departments and community-based organizations). The program also provides education, condom distribution, case management, data management, treatment, partner services, needs assessments, epidemiological studies, analysis, and research.
- Partners: Local health departments, various community-based organizations, Indian tribal governments, federal government, and Sexually Transmitted Disease Control Programs in other states.
Treatment and Care Services Program
- Goals: (1) reduce the incidence of tuberculosis in Utah through prompt identification and treatment of active tuberculosis cases, (2) provide a comprehensive health examination for newly arriving refugees, and (3) develop a more effective and cost-effective system for the delivery of essential services to individuals and families with HIV disease
- Target Populations: (1) individuals infected with HIV and/or tuberculosis without health insurance or are underinsured by private health insurance and do not qualify for Medicaid, Medicare, or other State or local programs and (2) newly arriving refugees
- Services Provided:
- HIV Services - AIDS-related medications, durable medical equipment, ambulatory out patient care, dental services, transportation, case management, and the Health Insurance Program. The Health Insurance Program pays all or part of a person's health insurance premium deductibles and pharmacy co-pays if the person has HIV disease and is eligible through COBRA or is in the insurance marketplace for their health benefits.
- Tuberculosis services - medications, medical expertise, and public health nursing (all provided at no charge).
- Refugees -- this program also administers the federally-funded Refugee Health Program, which provides health screening and follow-up to newly arriving refugees in the State. The program conducts health screenings to protect Utah's resident population from exposure to communicable diseases and related problems. In recent years refugees arriving in Utah have primarily come from Bhutan, Burma, Iraq, Iran, Somalia, Eritrea, Sudan, Congo, and Afghanistan.
Communicable Disease Investigation and Response Program (CDIRP)
The Communicable Disease Investigation and Response Program (CDIRP) conducts communicable disease surveillance and management. The responsibilities of the CDIRP include assisting with the identification, investigation, and management of communicable diseases and outbreaks. The program conducts epidemiological investigations in collaboration with local health departments to identify risk factors and implement appropriate control measures and prevention strategies. The program also responds rapidly to suspect and confirmed cases of diseases of public health significance, aiding local health departments, healthcare workers, and the public in implementing control and prevention measures. In addition, the program provides consultation regarding communicable diseases to healthcare professionals, healthcare facilities, and a variety of local, State, and federal agencies, and acts as a liaison to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for disease investigations in Utah.
Communicable Disease Analysis and Reporting Program
The Communicable Disease Analysis and Reporting Program conducts regular analyses of surveillance data as well as generating and evaluating daily reports. These reports incorporate statistical methods to interpret disease trends over time to identify clusters of disease that may indicate an outbreak or bioterrorism event. The program also develops surveillance reports that provide communicable disease trend data to the public, healthcare professionals, and local, State, and federal partners on a regular basis and as requested.
The program is responsible for maintaining Utah's National Electronic Database Surveillance System for Surveillance (UT-NEDSS) and providing support to local health departments in using this system to store and manage communicable disease data. The program is also responsible for building, implementing, and maintaining the UT-NEDSS in Utah as part of a national effort to improve mechanisms for disease reporting, public health surveillance, and disease control practices. UT-NEDSS provides a web-based system for storing and managing communicable disease data. UT-NEDSS also allows local and State Health Department staff to simultaneously monitor and evaluate case management functions. The program also is responsible for Utah's participation in the National Notifiable Disease Surveillance System managed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Environmental Epidemiology Program
The Environmental Epidemiology Program addresses environmental hazards and diseases in Utah. The mission of the program is to improve the health of Utah residents through science-based environmental policy and by empowering citizens through knowledge about environmental health risks and concerns. The program works with the Utah Department of Environmental Quality and other state and federal agencies to prevent or reduce the potential for acute and chronic morbidity and mortality associated with environmental and occupational factors, including exposure to toxic substances and radioactive and other agents responsible for debilitating diseases. The program conducts epidemiological and toxicological investigations; develops, produces and distributes educational awareness materials about environmental health concerns to the public; cooperates with local, State, and federal agencies in investigating and resolving health concerns related to hazardous substance exposure, and researches environmental and occupational health concerns.
Environmental Sanitation Program
The Environmental Sanitation Program's goal is to primarily prevent and/or reduce illness, premature death, and disability due to the effects of secondhand smoke, contaminated food, and poor sanitation at public food service establishments, public swimming pools, public lodging, schools, and many other public places. With the focus to decrease illness, premature death, and disability due to contaminated food served to the public, this program provides consultation to food and restaurant inspectors. This program also seeks to establish and maintain a consistent approach statewide to environmental health regulation across the 12 local health departments in Utah through implementing rules and consultation and training aimed at a standardized approach to enforcement.
The Immunization Program promotes vaccinations as part of comprehensive health care across the life span: infants, children, adolescents, and adults. It provides services through technical assistance to local health departments (LHD), community health centers, managed care organizations, schools (public and private), and early childhood programs (licensed day cares, head start, etc.), as well as other providers. The program contracts with LHDs and community health centers to support activities to increase immunization coverage rates for eligible populations. Special emphasis is placed on efforts to improve the immunization coverage of preschool-age children and adolescents, especially those less than two years of age via local coalitions and media campaigns. Additionally, the program monitors required school entry vaccination levels of all school children kindergarten through grade 12 in collaboration with the Utah State Office of Education.
The Immunization Program also performs the following functions:
- Monitors the incidence of vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Assists in preparing for and addressing disease outbreaks.
- Maintains the Immunization Hotline.
- Supports the operation of the Utah Statewide Immunization Information System.
- Provides educational information and technical assistance to all of Utah through grant-awarded Centers for Disease Control and Prevention funds.
- Manages the Utah Vaccines for Children Program.
The federally-funded Vaccines for Children Program provides vaccines at no cost to eligible children ages 0-18 years that are uninsured, covered by Medicaid, under-insured, or American Indian. The vaccine is provided to over 350 enrolled public and private medical providers statewide. This program provides technical assistance for vaccine management and accountability including: doses administered, quality assurance, assessment, storage and handling, and audits. CHIP uses the Vaccines for Children distribution system to provide vaccines which provides a substantial cost savings to the CHIP program and provides the same services related to vaccine management and accountability. The federal government also maintains the Vaccine Adverse Event Reports System, which provides for a reporting system for adverse events following receipt of any U.S. licensed vaccine.
Utah Statewide Immunization Information System
Utah Statewide Immunization Information System is a web-based system that collects, consolidates, and maintains immunization records for Utah residents. Health care providers can use the system to prevent over and under immunization. The system facilitates the introduction of new vaccines, implements changes in medically-recommended vaccine schedules, as well as tracking vaccines during shortages and recalls. The system is also used by public and private schools, daycares and camps to assist with meeting school and childcare immunization rules. The program develops, operates and supports the system, as well as data interfaces to electronic health record systems operated at private practices, public clinics, pharmacies and other collaborating programs. The Health Department uses this data to monitor the overall immunization rates in Utah and to assist with outbreak management.
Healthcare Associated Infections Prevention and Reporting Program
Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) are infections that patients acquire during the course of receiving healthcare treatment for other conditions. These infections related to medical care can be devastating and even deadly. The Healthcare Associated Infections Prevention and Reporting Program strives to understand the burden of HAIs within the state, how these infections occur and work collaboratively with healthcare facilities, local public health departments, and other partners toward their reduction and elimination.
The program uses HAI data reported by healthcare facilities to the National Healthcare and Safety Network to compile an annual report for public distribution. An annual report is also compiled for public distribution detailing healthcare worker influenza vaccination rates in acute care facilities.
The HAI program is responsible for development and revision of R386-705, the Health Care Associated Infection Rule, which identifies Utah's reporting requirements related to healthcare associated infections with data sharing requirements for HAI data reported by facilities to the National Healthcare and Safety Network.
COBI contains unaudited data as presented to the Legislature by state agencies at the time of publication. For audited financial data see the State of Utah's Comprehensive Annual Financial Reports.