The Division of Solid and Hazardous Waste protects public health and the environment by ensuring proper management of solid wastes, hazardous wastes, and used oil within Utah.
During the 2015 General Session, the Legislature appropriated for Fiscal Year 2016, $0 from all sources for Solid and Hazardous Waste. This is a 100 percent reduction from Fiscal Year 2015 revised estimated amounts from all sources.
In addition to statewide compensation and internal service fund cost increases, the following appropriation adjustments were made during the 2015 General Session:
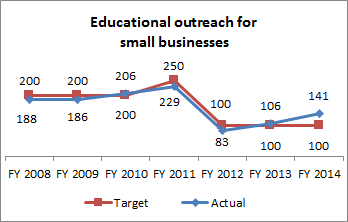
Educational Outreach to Small Businesses
Small businesses typically do not have the resources to hire environmental professionals to manage their regulatory affairs. The division provides technical assistance to help these businesses understand their regulatory responsibilities and find ways to reduce costs through proper waste management, waste reduction, and recycling. Educational and technical assistance also reduces or eliminates releases of hazardous wastes through improper disposal. This measure below shows the educational outreach and technical assistance to small businesses. The reduced target for FY 2012 reflects the smaller amount of small businesses and the reduction in staff within the division.
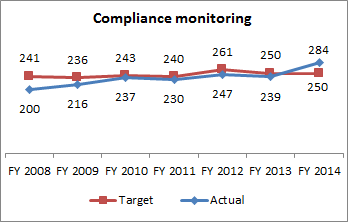
Hazardous Waste Compliance Monitoring
Protection of human health and the environment requires compliance with regulatory standards. This measure shows the number of compliance inspections at facilities that generate, store, treat, and dispose of hazardous waste, solid waste, and used oil. The increase in the FY 2012 target reflects the increase in the number of solid waste facilities throughout the state.
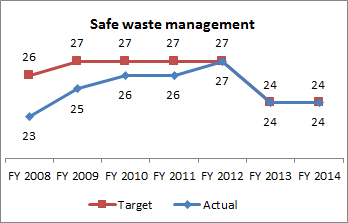
Hazardous Waste Management Permits
Facilities that treat, store, or dispose of hazardous waste require permits. Permits contain conditions for waste management that ensure protection of human health and the environment. This measure shows the issuance of hazardous waste management permits for all facilities subject to permitting requirements. NOTE: The reduction in the FY 2013 target reflects the termination of three permits (facilities closed; therefore, permits were no longer needed).
Other Solid and Hazardous Waste Performance Measures
In addition to the key performance measures listed above, the division reported the following performances measures for FY 2014:
- regulated 10,500 tons of hazardous waste;
- regulated 605 tons of chemical agent waste;
- regulated 14,674 tons of PCB-contaminated waste;
- regulated 3.8 million tons of non-hazardous waste;
- recycled 12.3 million gallons of used oil;
- recycled 139.14 pounds of mercury;
- recycled 2.0 million waste tires; and,
- managed 247 solid waste, hazardous waste and used oil permits, waste tire transporters and recycler registrations, and approved plans of operation.
In order to accomplish its mission, the division does the following:
- issues and modifies permits for solid waste, hazardous waste, and used oil management facilities;
- reviews and approves risk assessments, corrective action, and cleanup and closure plans;
- conducts on-site compliance inspections;
- responds to complaints and emergencies;
- maintains state program authorization and develops and updates regulations and guidance documents;
- provides technical assistance;
- collects and distributes waste management data;
- administers the Used Oil program;
- administers the Waste Tire Recycling program;
- administers the Mercury Switch Removal program;
- administers a Compliance Assistance Program for small businesses;
- administers the Corrective Action Program; and
- provides oversight of the Lead Acid Battery Recycling program
The division is responsible for administering the comprehensive solid and hazardous waste management program as established by state and federal law. The division administers the Federal Solid and Hazardous Waste program through delegation from the federal government. It also administers several state established waste programs related to solid waste, used oil, mercury switches, lead acid batteries, and waste tires.
Solid Waste
The division has the statutory responsibility to develop a state solid waste management program. The main areas of concentration in solid waste management are planning, permitting, compliance, closure/post closure care, technical assistance, and complaint response.
Permitting:
State law requires that all solid waste disposal facilities (e.g. sanitary landfills, municipal solid waste incinerators, non-hazardous industrial waste landfills, medical waste incinerators, etc.) have permits from the division. Division staff works with local government and industry to ensure proper construction and operation of these facilities.
Compliance:
All facilities that manage solid waste are inspected on a regular basis to maintain regulatory compliance and to ensure protection of human health and the environment.
Closure/Post-closure Care:
All facilities that have disposed of solid waste must close at the end of operations in accordance with standards which provide protection of human health and the environment. Monitoring and site maintenance after closure are required to ensure continued protection from contamination.
Technical Assistance:
Solid waste staff responds to request for assistance from the public, local government, and industry. All complaints are investigated.
Hazardous Waste
The division has the statutory responsibility to develop a comprehensive hazardous waste management program. The main areas of concentration in hazardous waste management are permitting, compliance, corrective action, closure/post closure and technical assistance.
Permitting:
All facilities which treat, store or dispose of hazardous waste must have a permit issued under the Utah Solid and Hazardous Waste Act.
Compliance:
All facilities which have hazardous waste permits and facilities that generate hazardous waste are inspected on a regular basis to maintain regulatory compliance and to ensure protection of human health and the environment.
Corrective Action:
Companies who have releases from their hazardous waste management units are required to initiate corrective action measures to eliminate any problems caused. These activities must be approved by the division.
Technical Assistance:
Hazardous waste staff responds to requests for assistance from the public, local government, and industry. The division investigates an average of 200 complaints per year concerning mismanagement of hazardous waste.
Closure/Post-closure Activities:
All facilities that have treated, stored, or disposed of hazardous waste must close in accordance with standards which provide protection of human health and the environment. Monitoring and site maintenance after closure are required to ensure continued protection from contamination.
Used Oil Program:
This program was established under the 1993 Used Oil Management Act to promote used oil recycling and to protect human health and the environment. Program components include permitting, compliance inspections, corrective action, cleanup and closure, spill response, and technical assistance. The program has resulted in the recycling of approximately 12 million gallons of used oil per year in Utah.
Waste Tire Recycling Program:
The division encourages the recycling of waste tires and oversees the waste tire disposal ban, the registration of tire transporters, and waste tire recyclers. The division also oversees the cleanup of waste tire piles and reimbursement of cleanup and recycling costs, as required by the Waste Tire Recycling Act. Additionally the program monitors and enforces waste tire rules. Approximately two million tires are recycled annually in Utah.
Mercury Switch Removal Program:
The division administers the Mercury Switch Removal Program. The program provides standards for removal and management of mercury switches from automobiles. The switches are processed for reclamation of mercury. Participants are reimbursed for each switch removed. To date, over 63,200 switches have been removed and sent to mercury recyclers, representing over 139 pounds of mercury removed from the environment.
Compliance Assistance Program:
The division administers a compliance assistance program for small businesses that generate hazardous waste. The program is designed to help small businesses understand and comply with applicable regulations. Technical assistance is provided in areas of waste reduction, onsite storage, process improvement, management standards and disposal options. There is no enforcement component associated with this program.
Lead Acid Battery Program:
The division oversees the lead acid battery recycling program and enforces the ban on landfilling of these batteries. This program has resulted in the recycling of most waste lead acid batteries generated in Utah.
COBI contains unaudited data as presented to the Legislature by state agencies at the time of publication. For audited financial data see the State of Utah's Comprehensive Annual Financial Reports.